LightOJ 1257 - Farthest Nodes in a Tree (II)
Prerequisite:
1) Graph Theory
2) DFS
3) It is recommended to solve the problem LightOJ 1094 - Farthest Nodes in a Tree before solving this problem.
What the problem wants:
For each node, you have to find another node in the undirected and weighted graph so that their intermediate distance is maximum and you have to print that distance for all nodes.
How to solve:
Consider this sample:
9
3 5 18
3 1 1
1 0 30
1 8 8
1 6 56
0 4 31
4 7 58
0 2 58
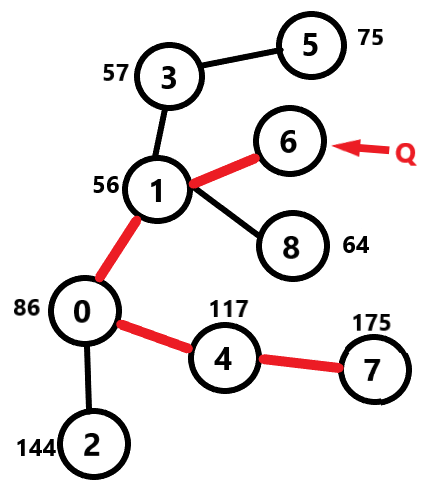
This sample can be represented in a graph like below:
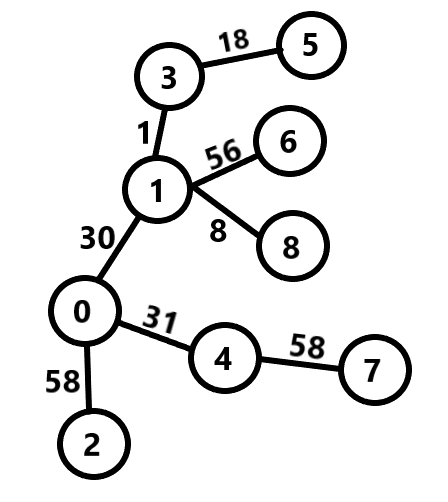
1) Take a random node S as source and apply DFS. Find the node which is farthest from the source node. Suppose we got the node P which is farthest from the source node S.
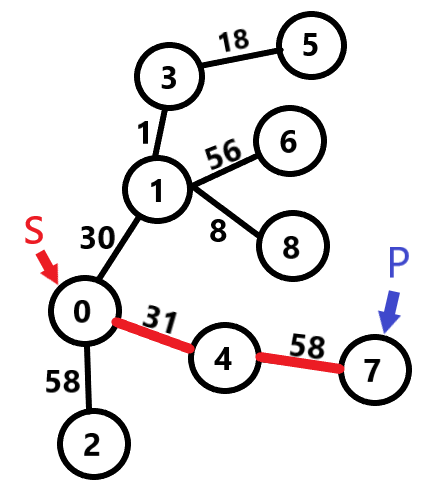
Suppose we have taken node 0 as S.
Distance from 0 to 5 is 30+1+18 = 49`` <br>
Distance from `0` to `6` is30+56 = 86<br>
Distance from `0` to `8` is30+8 = 38<br>
Distance from `0` to `7` is31+58 = 89which is the maximum distance we can get from the source node `0`. So `P` wil be node `7`. <br>
2) Take `P` as source and apply DFS again to find the farthest node from `P` which can be called `Q`. Similarly we can easily figure out that distance from node `7` to node `6` is greater than any other node connected to `7`. So our `Q` is `6`. While applying DFS, we can store the distance of every node from the source node `P` in an array. Let it's name `P_diff`. <br>
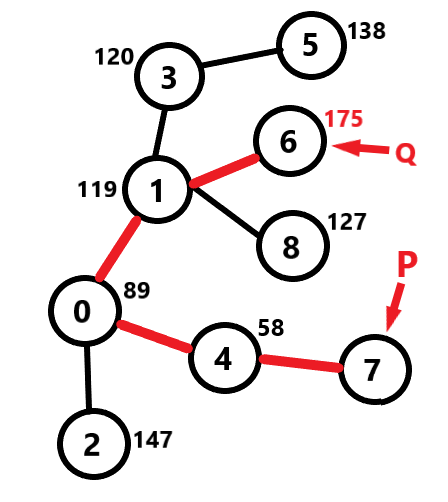 <br>
 <br>
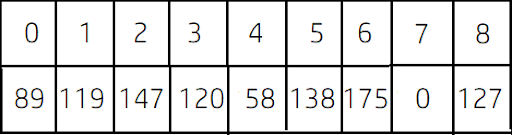
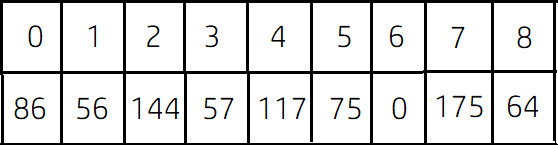
3) Apply DFS for the last time taking `Q` as source node and similarly as before, we can store the distance of every node from the source node in an array. Let it's name `Q_diff`. <br>
 <br>
 <br>
4) Maximum distance for every node should be themax(P_diff[i], Q_diff[i])``` where i from 0 to n-1.
Explanation:
Suppose there are some linear nodes and distance of each two neighbouring nodes is given:
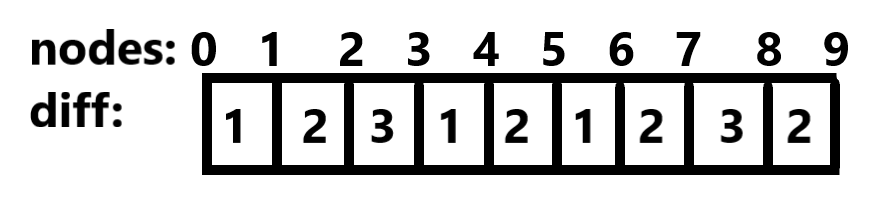
Now what will be the maximum distance from node 5? Distance between node 0 and node 5 is 1+2+3+1+2 = 9 and distance between node 5 and node 9 is 1+2+3+2 = 8. If we observe, we can see that, maximum distance for each node will be either distance from node 0 or distance from node 9.
Similarly, in a graph, maximum distance for each node is either distance from node P or distance from node Q where distance between P and Q is the maximum possible distance in the graph. Suppose for a node U, there can be two types of case:
1) U lies on the path PQ. In this case, maximum distance from node U will obviously be either node P or node Q because PQ is the diameter of the graph. If we assume there is a node V and UV is not a diameter(UV < PQ) and distance from U and V is farthest.
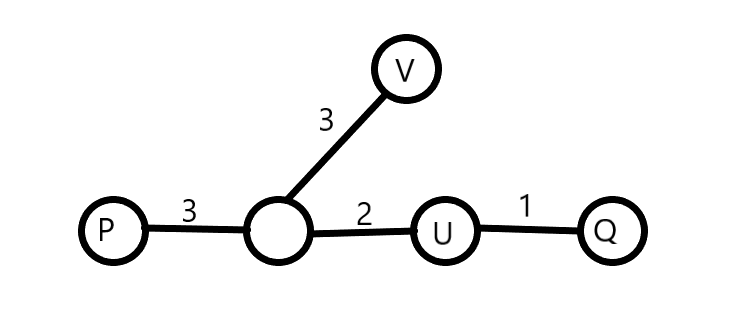
So, it means either UV > UP or UV > UQ. Let, UV is greater than UP, so UV + UQ > UP + UQ which means UV + UQ > PQ which is a contradiction because PQ is the maximum possible distance in the graph. So, maximum distance from node U is either node P or node Q.
2) U doesn't lie on the path PQ. So, obviously U lies on a subchain that starts from any node on the diameter, let it X. Let farthest node from node U is node V which also lies on a subchain that starts from any node on the diameter, Let it Y.
As, PQ is the maximum possible distance i.e. diameter of the graph, PX >= UX and QY >= VY.
So, if we think UV is the maximum possible distance from node U that means, UX + XY + VY > UX + XY + QY.
that means, VY > QY which is a contradiction because diameter always follows the maximum distance. So, Q is the farthest node from node U. We can prove similarly for node P.
In this way, we can prove that maximum distance from every node U is either node P or node Q.
You can try out the above sample on How to solve. Try to find a node, for which the farthest node is not P or Q.
Solution in C++:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<pair<ll, ll> > adj[30005];
ll vis[30005] = {0} ;
ll dif[30005];
ll mx = 0, mxnode ;
void dfs(ll s, ll d)
{
vis[s] = 1 ;
dif[s] = max(d, dif[s]) ;
if(d>mx)
{
mx = d ;
mxnode = s ;
}
ll i;
for(i=0; i<adj[s].size(); i++)
{
if(vis[adj[s][i].first] == 0)
{
dfs(adj[s][i].first, d+adj[s][i].second);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
ll tc, k;
cin >> tc ;
for(k=0; k<tc; k++)
{
ll n;
cin >> n ;
for(i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
ll a, b, w ;
cin >> a >> b >> w ;
adj[a].push_back({b,w});
adj[b].push_back({a,w});
}
int P, Q ;
int P_diff[n+1], Q_diff[n+1];
mx = 0;
dfs(0, 0);
P = mxnode ;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
mx = 0;
dfs(P, 0);
Q = mxnode ;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
P_diff[i] = dif[i];
}
memset(dif, 0, sizeof dif);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
dfs(Q, 0);
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
Q_diff[i] = dif[i];
}
cout << "Case " << k+1 << ":" << endl;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cout << max(P_diff[i], Q_diff[i]) << endl;
}
memset(adj, 0, sizeof adj);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
memset(dif, 0, sizeof dif);
}
return 0;
}
Solution in Python: (Thanks to Shanto Tanzim for the solution)
dis=[0]*30005
vis=[0]*30005
def explore(i,d):
x=0
y=0
z=0
dis[i]=d
stk=[i]
while stk:
i=stk.pop()
for j in range(len(a[i])):
x=a[i][j][0]
w=a[i][j][1]
if not vis[x]:
vis[x]=1
dis[x]=dis[i]+w
stk+=x,
#explore(x,d+w)
def routine(start):
ans=0
for i in range(30005):
vis[i]=0
dis[i]=0
maxi=-1
vis[start]=1
explore(start,0)
for i in range(n):
if dis[i]>maxi:
maxi=dis[i]
ans=i
return ans
for cs in range(int(input())):
n=int(input())
a=[[] for i in range(n+5)]
for i in range(n-1):
x,y,w=map(int,input().split())
a[x]+=[y,w],
a[y]+=[x,w],
k1=routine(0)
k2=routine(k1)
c=[0]*30005
for i in range(n):
c[i]=dis[i]
k3=routine(k2)
print("Case",str(cs+1)+":")
for i in range(n):
print(max(dis[i],c[i]))
Solution in Java: (Thanks to Zahid Hasan for the solution)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.io.DataInputStream ;
import java.io.FileInputStream ;
import java.io.IOException ;
public class A {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Reader scan = new Reader();
int t = scan.nextInt();
int q = 1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (t-- > 0) {
mx = 0;
int n = scan.nextInt();
ArrayList<Node>[] node = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
node[i] = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
addEdge(scan.nextInt(), scan.nextInt(), scan.nextInt(), node);
}
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[n];
findDiameter(a, b, node, n);
sb.append("Case " + q++ + ":\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sb.append(farNode(i, a, b) + "\n");
}
System.gc();
}
System.out.println(sb.delete(sb.length() - 1, sb.length()));
}
static void addEdge(int u, int v, int w, ArrayList<Node>[] node) {
{
node[u].add(new Node(v, w));
node[v].add(new Node(u, w));
}
}
static int currNode;
static int mx = 0;
static void findDiameter(int[] xDis, int[] yDis, ArrayList<Node>[] node, int n) {
findDiameterHelper(0, 0, xDis, node, n);
int x = currNode;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
xDis[i] = 0;
}
mx = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
findDiameterHelper(x, 0, xDis, node, n);
int y = currNode;
mx = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
findDiameterHelper(y, 0, yDis, node, n);
}
static int farNode(int u, int[] xDis, int[] yDis) {
return Math.max(xDis[u], yDis[u]);
}
static void findDiameterHelper(int u, int w, int[] arr, ArrayList<Node>[] node, int n) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(u);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
vis[u] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int curr = q.poll();
if (arr[curr] > mx) {
mx = arr[curr];
currNode = curr;
}
vis[curr] = true;
for (Node child : node[curr]) {
if (!vis[child.v]) {
arr[child.v] = child.w + arr[curr];
q.add(child.v);
}
}
}
}
}
class Node {
int v;
int w;
Node(int a, int b) {
v = a;
w = b;
}
}
class Reader {
final private int BUFFER_SIZE = 1 << 16;
private DataInputStream din;
private byte[] buffer;
private int bufferPointer, bytesRead;
public Reader() {
din = new DataInputStream(System.in);
buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
bufferPointer = bytesRead = 0;
}
public Reader(String file_name) throws IOException {
din = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file_name));
buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
bufferPointer = bytesRead = 0;
}
public String readLine() throws IOException {
byte[] buf = new byte[64];
int cnt = 0, c;
while ((c = read()) != -1) {
if (c == '\n') {
break;
}
buf[cnt++] = (byte) c;
}
return new String(buf, 0, cnt);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
int ret = 0;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') {
c = read();
}
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg) {
c = read();
}
do {
ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
} while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (neg) {
return -ret;
}
return ret;
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
long ret = 0;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') {
c = read();
}
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg) {
c = read();
}
do {
ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
} while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (neg) {
return -ret;
}
return ret;
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
double ret = 0, div = 1;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') {
c = read();
}
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg) {
c = read();
}
do {
ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
} while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (c == '.') {
while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9') {
ret += (c - '0') / (div *= 10);
}
}
if (neg) {
return -ret;
}
return ret;
}
private void fillBuffer() throws IOException {
bytesRead = din.read(buffer, bufferPointer = 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
buffer[0] = -1;
}
}
private byte read() throws IOException {
if (bufferPointer == bytesRead) {
fillBuffer();
}
return buffer[bufferPointer++];
}
public void close() throws IOException {
if (din == null) {
return;
}
din.close();
}
}
Tutorial source





